Foreword : The temperature and pressure sensor is composed of temperature sensitive components and detection lines. The temperature sensor can be roughly divided into two types: contact type and non-contact type. The former is to make the temperature sensor directly contact with the object to be measured to sensitively change the temperature of the measured object, and the latter is to make the temperature sensor and the test object to be tested. The object leaves a certain distance and detects the infrared rays emitted from the object to be tested, thereby achieving the purpose of temperature measurement.
Conventional thermocouples, RTDs, thermistors, and semiconductor temperature sensors convert the temperature value through a certain interface circuit to output an analog voltage or current signal. These voltage or current signals can be used for measurement control. Integrating the analog temperature sensor with the digital conversion interface circuit becomes a digital temperature sensor with digital output capability. With the rapid development of semiconductor technology, semiconductor temperature sensors are gradually integrated with corresponding conversion circuits, interface circuits and various other functional circuits to form a powerful, accurate and inexpensive digital temperature sensor.
Temperature sensor characteristicsTemperature sensor is a device for detecting temperature. It is widely used in industrial and agricultural production, scientific research and life, etc. It has many types and develops rapidly. Temperature sensors are generally divided into contact and non-contact types. The so-called contact type is that the sensor directly contacts the object to be measured for temperature measurement, which is the basic form of temperature measurement. Non-contact type is the infrared ray emitted by measuring the heat radiation of an object to measure the temperature of the object. It can be telemetry, which is not possible by the contact method. Contact temperature sensors include thermocouples, thermistors, and platinum resistors. They are used in household appliances, automobiles, ships, control equipment, and industrial industries to measure the temperature of objects using their thermoelectromotive force or resistance as a function of temperature. Measurement, communication equipment, etc. In addition, there are some newly developed sensors, such as semiconductor integrated sensors that utilize semiconductor PN junction current/voltage characteristics as a function of temperature; there are fiber propagation characteristics that vary with temperature or semiconductors.
Optical fiber sensor with light transmission change with temperature; sensor with elastic surface wave and oscillator's oscillation frequency changing with temperature; NQR sensor with oscillation frequency of nuclear quadruple resonance with temperature; use magnetic sharp change near Curie temperature Magnetic temperature sensor and sensor that uses liquid crystal or paint color to change with temperature. The non-contact method measures the temperature of an object by detecting infrared rays in the photosensor, and has a quantum type that absorbs light by a semiconductor and a thermal type sensor that absorbs light and causes temperature change. Non-contact sensors are widely used in contact temperature sensors, radiation thermometers, alarm devices, visitor informants, fire alarms, automatic doors, gas analyzers, spectrophotometers, resource detection, etc. The company specializes in the production of various temperature sensor series: thermocouple, thermal resistance, bimetal thermometer, temperature transmitter series, etc. Welcome customers to come to the selection. Temperature sensor principle
First, the application principle of temperature sensor thermocoupleTemperature sensor thermocouples are one of the most commonly used temperature sensing components in the industry. The advantages are:
1 Measurement accuracy is high. Because the temperature sensor thermocouple directly contacts the object to be tested, it is not affected by the intermediate medium.
2 Wide measurement range. Commonly used temperature sensor thermocouples can be continuously measured from -50 to +1600 °C. Some special temperature sensor thermocouples can measure -269 °C (such as gold-iron nickel-chromium), up to +2800 °C (such as tungsten-bismuth). ).
3 simple structure, easy to use. Temperature sensor thermocouples are usually made up of two different wires and are not limited by size and opening. They have a protective sleeve and are very convenient to use.
1. Temperature sensor thermocouple temperature measurement basic principle
Conducting conductors or semiconductors A and B of two different materials to form a closed loop. When there is a temperature difference between the two attachment points 1 and 2 of conductors A and B, an electromotive force is generated between the two, and thus the loop A current of one size is formed, which is called a thermoelectric effect. Temperature sensor thermocouples use this effect to work.
2. Temperature sensor thermocouple type and structure formation
(1) Types of temperature sensor thermocouples
Commonly used temperature sensor thermocouples can be divided into two categories: standard temperature sensor thermocouples and non-standard temperature sensor thermocouples. The so-called standard temperature sensor thermocouple refers to the temperature sensor thermocouple that the national standard specifies the relationship between the thermoelectric potential and the temperature, the allowable error, and the uniform standard index table. It has a display instrument that is compatible with it. Non-standardized temperature sensor thermocouples are inferior to standardized temperature sensor thermocouples in terms of use range or magnitude. Generally, there is no uniform indexing table, which is mainly used for measurement in some special occasions. Standardized Temperature Sensor Thermocouples Since January 1, 1988, temperature sensor thermocouples and temperature sensor thermal resistors have all been produced in accordance with IEC international standards, and seven standard temperatures of S, B, E, K, R, J, and T have been specified. The sensor thermocouple is a unified design temperature sensor thermocouple in China.
(2) Structural form of temperature sensor thermocouple
In order to ensure reliable and stable operation of the temperature sensor thermocouple, its structural requirements are as follows:
1 The welding of the two hot electrodes that make up the temperature sensor thermocouple must be firm;
2 The two hot electrodes should be well insulated from each other to prevent short circuits;
3 The connection between the compensation wire and the free end of the temperature sensor thermocouple should be convenient and reliable;
4 The protective sleeve should ensure that the hot electrode is sufficiently isolated from harmful media.
3. Temperature sensor thermocouple cold junction temperature compensation
Because the temperature sensor thermocouple material is generally more expensive (especially when using precious metals), and the temperature measurement point is far away from the meter, in order to save thermocouple materials and reduce costs, the compensation wire is usually used to charge the temperature sensor thermocouple. The cold end (free end) extends into a relatively stable temperature control chamber and is connected to the meter terminals. It must be pointed out that the function of the temperature sensor thermocouple compensation wire only extends the hot electrode, so that the cold end of the temperature sensor thermocouple moves to the instrument terminal of the control room, which itself cannot eliminate the influence of the temperature change of the cold end on the temperature measurement, Take compensation. Therefore, other correction methods are needed to compensate for the influence of the cold junction temperature t0 ≠0 ° C on the temperature measurement.
When using the temperature sensor thermocouple compensation wire, you must pay attention to the model matching, the polarity can not be connected wrong, the temperature of the compensation wire and the temperature sensor thermocouple connection terminal can not exceed 100 °C.
Second, the application principle of temperature sensor thermal resistanceTemperature sensor Thermistor is the most commonly used temperature detector in the low temperature zone. Its main features are high measurement accuracy and stable performance. Among them, platinum thermal resistance has the highest measurement accuracy, and it is not only widely used in industrial temperature measurement, but also made into a standard reference instrument.
1. Temperature sensor thermal resistance temperature measurement principle and material
Temperature sensor Thermistor temperature measurement is based on the fact that the resistance value of a metal conductor increases as the temperature increases. Temperature sensor thermal resistance is mostly made of pure metal materials. Currently, platinum and copper are the most widely used. In addition, temperature sensor thermal resistances have been fabricated using materials such as dian, nickel, manganese and tantalum. For example, Omega's PT100 temperature sensor includes a 100 ohm platinum resistance temperature probe.
2. Temperature sensor thermal resistance structure
(1) Mastery temperature sensor Thermal resistance Industrial temperature sensor Thermal resistance temperature sensing element (resistance body) From the temperature measurement principle of the temperature sensor thermal resistance, the change of the measured temperature is directly through the change of the resistance of the temperature sensor. Measured, therefore, changes in the resistance of various wires, such as the lead wire of the temperature sensor's thermal resistance, can affect the temperature measurement. In order to eliminate the influence of lead resistance, a three-wire system or a four-wire system is generally used.
(2) Armored temperature sensor Thermistor armored temperature sensor Thermistor is a solid body composed of a temperature sensing element (resistor), a lead wire, an insulating material, and a stainless steel bushing. Its outer diameter is generally φ2~φ8mm. The minimum is φmm.
Compared with the ordinary type temperature sensor thermal resistance, it has the following advantages: 1 small volume, no air gap inside, thermal inertia, small measurement lag; 2 good mechanical properties, vibration resistance, impact resistance; 3 can be bent, easy to install 4 long life.
(3) End face temperature sensor Thermistor end face temperature sensor The thermal resistance temperature sensing element is wound by a specially treated resistance wire and is closely attached to the end face of the thermometer. Compared with the general axial temperature sensor thermal resistance, it can reflect the actual temperature of the tested end face more correctly and quickly, and is suitable for measuring the end face temperature of the bearing bush and other parts.
(4) Explosion-proof temperature sensor Thermistor explosion-proof temperature sensor Thermistor is limited to the explosion in the junction box by the special structure of the junction box, and the explosion of the explosive mixture inside the casing is affected by the spark or arc. Will lead to an explosion. Explosion-proof temperature sensor RTD can be used for temperature measurement in explosion-prone areas in the Bla~B3c class.
3. Temperature sensor thermal resistance temperature measurement system
Temperature sensor Thermistor temperature measurement system generally consists of a temperature sensor thermal resistance, a connecting wire and a display instrument. The following two points must be noted:
1The temperature sensor thermal resistance and the display instrument's index number must be the same
2 In order to eliminate the influence of the change in the resistance of the connecting wire, a three-wire connection method must be used.
Main types of temperature sensorsThere are four main types of temperature sensors: thermocouples, thermistors, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and IC temperature sensors (see table below). The IC temperature sensor includes two types of analog output and digital output.
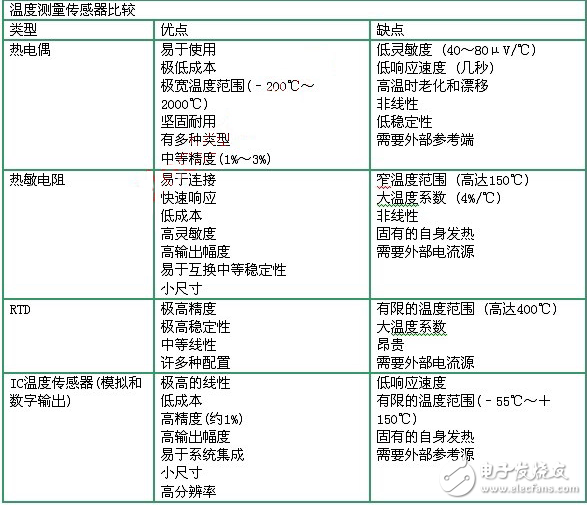
Thermocouples are widely used because they are very strong and not too expensive. There are many types of thermocouples that cover a very wide temperature range from -200 °C to 2000 °C. They are characterized by low sensitivity, low stability, medium accuracy, slow response, easy aging and drift at high temperatures, and non-linearity. In addition, the thermocouple requires an external reference.
The RTD is extremely accurate and has moderate linearity. They are particularly stable and come in many configurations. But their maximum operating temperature can only reach about 400 °C. They also have large TCs and are expensive (4 to 10 times that of thermocouples) and require an external reference source.
The analog output IC temperature sensor has a high degree of linearity (if an analog to digital converter or ADC can produce a digital output), low cost, high precision (about 1 [[%]]), small size and high resolution. Their shortcomings are limited temperature range (-55 ° C ~ +150 ° C) and require an external reference source
The digital output IC temperature sensor has a built-in reference source and their response speed is also quite slow (on the order of 100 ms). Although they inherently generate heat themselves, auto-shutdown and single-shot modes can be used to set the IC to a low-power state before measurements are needed, thereby minimizing self-heating.
Compared to thermistors, RTDs, and thermocouple sensors, the IC temperature sensor has high linearity, low system cost, and integrated complex functions to provide a digital output and temperature measurement in a fairly useful range.
Pure Sine Wave Inverter,Pure Sine Wave Power Inverter,Dc Pure Sine Inverter,Reliable Pure Sine Wave Inverter
GuangZhou HanFong New Energy Technology Co. , Ltd. , https://www.gzinverter.com