Current can cause multiple injuries to the human body. For example, when the current passes through the human body, the human body directly receives the current energy and is subjected to electric shock; the electric energy is converted into heat energy to the human body, causing the human body to be burned or burned; when the human is irradiated by the electromagnetic field, the energy of the electromagnetic field is also damaged. Among the many injuries, the damage of electric shock is the most basic form.
Unlike some other injuries, current damage to the human body does not have any warning in advance. The damage often occurs between the moments, and the damage to the human body is rapidly reduced once it is subjected to an electric shock. Both of these features increase the risk of current damage.
1 Current damage to the human body The damage to the human body is usually the electric shock. It is the energy of the current directly acting on the human body or converted into other forms of energy to cause damage to the human body.
1.1 Electric shock The electric shock is the current passing through the human body, the body tissue is stimulated, and the muscles involuntarily cause the injury caused by the spasmodic contraction. Severe electric shock refers to the destruction of the normal work of the human heart and the nervous system of the lungs, and even life-threatening injuries. The power frequency of tens of milliamps can cause a fatal electric shock. The part of the electric shock is mainly inside the human body, and there is no obvious trace on the outside of the human body.
A power frequency alternating current of 50 mA (effective value) or more passes through the human body, and generally may cause ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest, or may cause breathing to stop. However, the former appears much earlier than the latter, that is, the former is the main one.
If the current through the human body is only 20~25mA, it will not directly cause ventricular fibrillation or the heart stops beating. However, if it takes a long time, it can still cause the heart to stop beating. At this time, ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest is mainly caused by hypoxia caused by the body's lack of oxygen. However, when the current through the human body exceeds several amps, the breathing may be stopped first due to strong stimulation. A few amperes of current flow through the body and can also cause severe burns and even death.
Electroconvulsive is a strong stimulation of the body, a strong nervous system reflex, causing obstacles in blood circulation, respiration and other metabolism, so that the nervous system is inhibited, blood pressure drops sharply, pulse is weakened, respiratory failure, conscious coma . The electroshock state can last for tens of minutes to several days. The consequences may be healing with effective treatment or death due to complete loss of vital vital functions.
1.2 Electrical injury is caused by the thermal, chemical and mechanical effects of current, and the current caused by electrical injury is relatively large. Electrical injuries can leave visible scars on the surface of the body, but the damage can go deep into the body.
Compared with electric shock, electric injury is a local injury. The degree of danger of electrical injury depends on factors such as the area of ​​injury, the depth of injury, and the location of injury.
Electrical injuries include electrical burns, electrocautery, skin metallization, mechanical damage, electro-optic eyes and many other injuries.
Electric burns are the most common electrical injury. Most electric shocks can cause electrical burns. Electric burns can be divided into electric burns and arc burns. The larger the current, the longer the energization time, and the smaller the resistance of the current path, the more severe the current burn. Because the area of ​​contact between the human body and the charged body is generally not large, and the skin resistance is relatively high, the contact between the skin and the charged body generates more heat and is severely burned. When the current is large, the subcutaneous tissue may be burned.
Because the breakdown discharge occurs when the high-voltage charged body is approached, current burns generally occur on low-voltage electrical equipment. Usually, hundreds of milliamperes of current can cause burns, and several amps of current will cause severe burns.
The electroless impression is a mark left at the contact area after the current passes through the human body. The skin at the scar is hard to change, losing its original elasticity and color, necrosis of the surface, and loss of consciousness.
Skin metallization is caused by the infiltration of metal particles into the skin. The injured part became rough and tight. Skin metallization occurs mostly during arc discharge and is generally injured in the exposed parts of the human body. When arc discharge occurs, skin metallization is not a major injury compared to arc burns.
Electro-optic manifestations of inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva. In the case of arc discharge, infrared rays, visible light, and ultraviolet rays may damage the eyes. For short-term exposure, ultraviolet light is the main cause of electro-optic eyes.
2 The current harm to the human body 2.1 The current through the different currents of the human body will cause different reactions of the human body. According to the habit, people usually divide the electric shock current into the sensing current, the reaction current, the current and the ventricular fibrillation current.
From a safety point of view, the man's permission to get rid of the threshold current is 9 mA, and the woman is 6 mA.
After the human body suffers from electric shock, the limit current that causes the probability of ventricular fibrillation greater than 5%, called the ventricular fibrillation threshold, is also called ventricular fibrillation current. When the shock time is less than 5 s, the ventricular fibrillation threshold can be calculated using the formula I=165/t1/2. When the shock time is greater than 5 s, 30 mA is used as another limit current value for causing ventricular fibrillation. A large number of tests have shown that the risk of ventricular fibrillation occurs when the shock current is greater than 30 mA.
2.2 The duration of the current passing through the human body The longer the electric shock is, the more serious the thermal, chemical and physiological damage caused by the current to the human body. In particular, the duration of current is closely related to ventricular fibrillation. According to the available data, the shortest electric shock time is 8.3ms, and there is very little more than 5s. From 5s to 30s, the limiting current causing ventricular fibrillation remained stable and decreased slightly. Longer shock time has no obvious effect on causing ventricular fibrillation, but has a greater impact on the risk of suffocation, thus reducing the lethal current.
In addition, the electric shock time is long, the body resistance is reduced due to sweating, etc., resulting in a further increase in the electric shock current, which will also increase the risk of electric shock.
2.3 When the current through the human body through the heart, the spine and the central nervous system and other vital parts, the electric shock is the most serious. Therefore, the most dangerous current path from left hand to chest and from left hand to right foot. From the right hand to the chest or from the right hand to the foot, from hand to hand, etc. are very dangerous current paths, from the foot to the foot is generally less dangerous, but does not mean that there is no danger. For example, due to the electric shock caused by the stride voltage, the starting current only passes between the two feet. After the electric shock, the electric foot will fall due to the severe smashing of the feet. At this time, the current will flow through other vital parts, which will also cause serious consequences; on the other hand, even if It is the electric shock of both feet, and some of the current will flow through the heart, which is also dangerous.
2.4 Influence of human body resistance Under the action of a certain current, the magnitude of the current flowing through the human body is inversely proportional to the body resistance. Therefore, the magnitude of the body resistance has a certain influence on the consequences of the electric shock. Human body resistance has the distinction of surface resistance and volume resistance. For electric shockers, the effect of volume resistance is most pronounced, but surface resistance sometimes has a certain inhibitory effect on the consequences of electric shock, causing it to be converted into electrical injury. This is due to the fact that the human skin is moist and the surface resistance is small, so that most of the current passes through the surface of the skin. In the past, it was considered that the more humid the human body is, the more harmful the electric shock is. This is not very accurate, because the effect of surface resistance on the consequences of electric shock is more complicated. Only when the total surface resistance is low, it is possible to suppress electric shock. Conversely, when the body is partially wet, especially if only the skin touching the live part is wet, the risk of electric shock is greatly increased. This is because the human body is partially moist, and does not have a great influence on the surface resistance value. The electric shock current does not shunt from the surface of the human body in a large amount, and the skin of the electric shock is wet, which will cause the volume resistance of the human body to decrease, and the harm of the electric shock is increased.
The skin resistance varies with conditions, and the magnitude of the change in body resistance is also large. When the human skin is dry, clean and harmless, the body resistance can be as high as 40~100kW; when the skin is in a damp state, such as wet hands, sweating, the body resistance will drop to about 1000W; if the skin is completely destroyed The body resistance will drop to around 600~800W.
2.5 Influence of current frequency
In addition to affecting the body's resistance, the frequency of the current also has a direct impact on the degree of damage from the shock. The AC of 25~300Hz is much more harmful to the human body than DC. At the same time, for AC, when it is lower or higher than the above frequency range, its damage will be significantly reduced.
2.6 Effects of human condition
The effect of current on the human body, women are more sensitive than men, and women's perception of current and current is about one-third lower than that of men. Because ventricular fibrillation current is approximately proportional to body weight, it is more dangerous for children to suffer from electric shock than adults.
The current-time effect partition of the alternating current through the human body is shown in Figure 1.
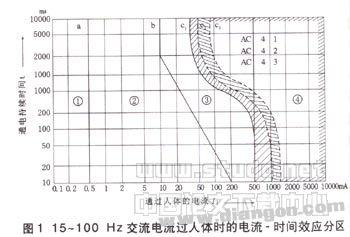
The effect of current flowing through the human body usually depends on the current amplitude and duration. Figure 1 shows the current amplitude-effect time effect partition map of the human body flowing through the human body.
The first effect area in the figure is based on the sensory threshold of the person's current, that is, the minimum current flowing through the human body that the human body can perceive. This sensory threshold depends on the contact area of ​​the human body with the electrodes, the contact state (dryness, humidity, pressure, temperature, etc.), the respective physiological characteristics of the person, and the like. The line a in the figure is the general sensory threshold line of the human body, which is equal to 0.5 mA, which is independent of the energization time. The left part of the a line is the first effect area, which usually does not have any pathological and physiological reactions to humans.
The second effect region is between the a line and the b line. The second effect zone usually has no harmful pathological and physiological reactions.
â‘¢ effect region between the first line and the c-line 1 b, the area in general no damage to human organs, but may produce muscle contraction, difficulty breathing, blood pressure, cardiac impulse formation and conduction reversibility disorders, including atrial fibrillation And non-ventricular fibrillation caused by an increase in current and duration, resulting in a brief cardiac arrest.
â‘£ effect region of the right portion of the curve c 1. In addition to the pathological and physiological responses of the third effector region, ventricular fibrillation may occur in this region. Curve c 1 is a threshold curve that does not cause ventricular fibrillation. From c 1 to the right, the probability of ventricular fibrillation gradually increases, reaching 5% and 50% at curves c 2 and c 3 , respectively, and more than 50% to the right. Ventricular fibrillation is considered to be the leading cause of electrocution. As the body's current and duration increase, there will be consequences such as cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, and severe burns. There is information that the heartbeat caused by human currents and suffocation may be fatal, and severe burns caused by several currents may also cause death.
According to the above effect partition, it is generally considered that the first and second effect zones are safe zones. The IEC provisions indicate that, from the operational experience of some countries, it is confirmed that the current flowing through the human body does not exceed 30 mA, and the duration does not exceed 0.1 s, which is safe for the human body. of.
Smart Phone Holder For Car Vent
Smart Phone Holder For Car Vent,Air Vent Iphone Mount,Air Vent Phone Holder,Air Vent Cell Phone Pouch Holder
Ningbo Luke Automotive Supplies Ltd. , https://www.nbluke.com