Some substations adopt RS-485 bus supporting multi-node remote communication as the communication network of local monitoring system, but the physical structure of 485 bus determines the mutual interference between nodes in the strong electromagnetic environment of substation. A topic to improve the reliability of the system.
Second, the impact of mutual interference between nodes on the busAll the lower computers on the 485 bus share a signal channel. This physical structure increases the common impedance coupling between the nodes, and mutual interference occurs between the nodes, thus greatly reducing the reliability of the system.
First of all, the transformer, the central control room and the transmission line of the substation will induce the interference voltage through the radiation on the surrounding communication line. When we measure a node A on the 485 bus, we find:
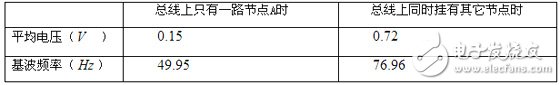
The measurement results show that the electromagnetic coupling between the nodes has a great influence on the amplitude and frequency of the induced voltage. Since the communication line is a twisted pair, the induced voltage on the two communication lines can be a common mode voltage having the same amplitude and phase. However, the twist of the twisted pair may not be exactly the same, and the pitch is not equal, so the differential mode voltage will appear between the lines. According to the cumulative common-mode voltage probability distribution map and probability formula provided in [1], the probability that the common-mode voltage falls into the differential-mode voltage is calculated, and the 485 driver/receiver receives the voltage. Therefore, the mutual interference between the nodes increases the value of the common mode voltage and the proportion of the differential mode signal, thereby increasing the probability of system malfunction.
Second, the transient electromagnetic field will be generated when the substation transformer is switched. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the transient voltage and current waveforms induced in a control signal line when a 500kV substation is disconnected.
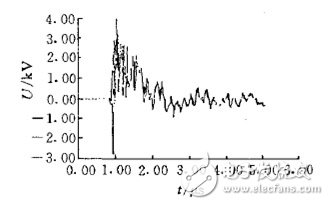
Figure 1 Transient voltage in the control line
Figure 2 Transient current in the control line
It can be seen that the instantaneous induced voltage/current on the signal line around the transformer or the node connected to it is much higher than the threshold voltage (12V)/current (250mA) of the 485 driver/receiver, so there is no good voltage limiting device. The 485 driver/receiver that will burn the node is more dangerous. The other nodes on the bus will pass through the coupling of the common circuit, which will inevitably induce the high voltage of the same amplitude, and all the nodes on the bus will be affected.
Finally, the substation outdoor communication cable shielding layer will be short-circuited due to natural wear, improper construction or malicious damage, resulting in a state of logic 0 on the bus. According to the RS-485 protocol, the lower computer interprets it as a new data start bit and tries to read subsequent data bits. Since there will never be a stop bit, this will produce a framing error result, so it will not Then there is a node requesting the bus, and the network will be in a state of paralysis.
Third, the solutionAlthough it is possible to improve the stability of the RS-485 bus by improving the on-site working environment of the substation, reducing electromagnetic pollution, increasing the voltage limiting device, and using short-circuit bias, etc., the entire bus system is not fundamentally isolated from the faulty node. Will not work, so only improve the reliability of the bus itself, to ensure the system works stably. Based on this, the 485 HUB star bus proposed in this paper completely isolates the nodes from the physical structure, and also improves the anti-interference ability from the software to reduce mutual interference.
3.1 Physical isolation
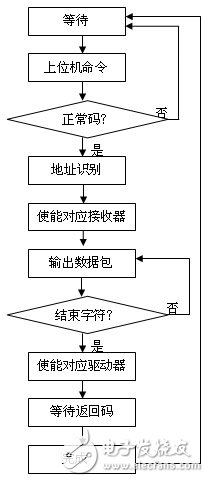
In the 485 HUB, the same number of 485 drivers/receivers as the lower computer are used, which correspond to all the nodes one by one, and each of them independently completes the task of transmitting/receiving data packets of the money node. First, the MCU on the HUB intercepts the data packet sent by the host computer, and after confirming the address, controls the 485 driver output enable end corresponding to the address node in the HUB, and then sends the intercepted data packet to the driver intact. After the transmission is completed, the drive is automatically converted to a receiver, waiting for feedback from the lower computer. The enable terminals of other 485 drivers/receivers in the HUB are not subject to control commands and do not change state. Only the strobed nodes communicate independently.
Schematic:

3.2 Software Design
In the program, multiple judgments of information, automatic inspection, system operation status monitoring, and automatic recovery at the time of failure occur, and errors and garbled characters caused by differential mode interference can be directly shielded after being identified by the program.
In order to prevent the program from being out of control and getting into an infinite loop, the time monitor Watchdog chip Max813L is used to monitor the running of the program and the power supply of the microcontroller.
Software flow chart:
3.3 Data isolation
The purpose of data isolation is to isolate the interference source from the susceptible part from the circuit, so that the field execution device maintains a signal connection with the upper control host, but does not directly make electrical contact. In the 485 HUB, a high-speed optocoupler isolator 6N137 is added to the loop of the feedback information so that various interfering pulses interposed in the input switching amount are blocked on one side of the output loop.
After using the 485 HUB, measure node A at the same position again. The measured values ​​are as follows:
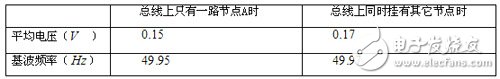
1. It can be seen from the measured values ​​that the interference between the nodes in the 485 HUB is significantly reduced, and the physical isolation ensures the independence of the nodes.
2. After trial and verification, even if a node has a short-circuit fault in the 485 HUB, other nodes can still work normally.
3. Due to the actual situation of the substation, this test does not capture the actual induced voltage of the HUB when the transformer is switched, but through the laboratory environment simulation, when the transient pulse voltage higher than the threshold of the driver appears on the communication line of a certain node Other nodes are not disturbed.
Therefore, the 485 HUB star bus ensures that when a node has strong electromagnetic interference or short circuit problems, it will not affect other nodes of the bus, improve the MTBCF, reduce the MTTR, and improve the reliability of the system.
Fourth, the conclusionIn terms of its physical structure, the 485 HUB star bus is different from the traditional 485 bus. Each 485 driver/receiver does not implement a multi-receiving bus function, but a point-to-point star connection. With the 485 HUB function, it can be said that the improvement of system reliability in this solution is at the cost of increasing the number of 485 drivers/receivers. However, the 485 HUB has a simple structure and low requirements on the working environment. Its high reliability and stability are particularly suitable for the remote control system of the substation, so it exceeds the traditional 485 bus in terms of cost performance.
RS-485 HUB star bus has been used in some substation remote control systems, with stable operation and improved anti-interference ability, which can meet the requirements of the site.
references:
[1] Electromagnetic compatibility theory and technology in the communication system of Lu Guizhen Jiang Kehua [M] Beijing Broadcasting Institute Press 2000
[2] Jan Axelson (I) Elite Technology (Translation) Serial Port Encyclopedia [M] China Electric Power Press 2001
[3] Sun Zhusen Zhang Yifang Zhang Guangzhou and other 500KV substation electromagnetic disturbance and protection measures (a) high voltage technology [J] February 2000
Easy Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.nbpcelectronicgroup.com