TAG management is an important issue in PCIE systems. User logic relies on the TAG to locate which Non-Posted transaction compleTIon corresponds to. Therefore, each outgoing Non-Posted operation must have its own separate TAG. In XILINX's Virtex-7 FPGA Gen3 Integrated Block, TAG management has some new features compared to the original Integrated Block for PCI Express v2.0, which must be taken care of.
In Integrated Block for PCI Express v2.0, the TAG is managed by user logic, and the user logic guarantees that the TAG of each Non-Posted transaction is unique and is responsible for checking the corresponding Non-Posted transaction from the TAG of the compleTIon. In the Gen3 Integrated Block, TAG management has two modes of operation.
The first mode of operation is to manage using the internal TAG manager. This mode of operation is selected by setting the AXISTEN_IF_ENABLE_CLIENT_TAG parameter to FALSE. It is also the default working mode. In this mode, the logic inside the Gen3 Integrated Block generates a TAG to the user-side Non-Posted transaction request. There is a list of available TAGs inside the Gen3 Integrated Block. When the user logic generates a Non-Posted transaction request on the interface, the Gen3 Integrated Block assigns a value in the available TAG to the Non-Posted transaction. At the same time, this TAG value appears on the pcie_rq_tag[5:0] interface to inform the user logic. The value of this port is valid when the Integrated Block sets pcie_rq_tag_vld high. The user logic must save the value of pcie_rq_tag to distinguish which Non-Posted transaction the compleTIon corresponds to. At the same time, the logic inside the Integrated Block checks if the TAG is exhausted and, when exhausted, backs up the user logic with the s_axis_rq_tready signal, preventing new Non-Posted transaction requests.
The second mode of operation is external TAG management. This mode of operation is selected by setting the AXISTEN_IF_ENABLE_CLIENT_TAG parameter to TRUE. In this mode of operation, the user logic must assign a TAG value to each Non-Posted transaction request. The user logic must ensure that the TAG value assigned to each Non-Posted transaction request is unique among all outgoing Non-Posted transactions. The TAG value informs the Gen3 Integrated Block via the descriptor of the transaction request. The Gen3 Integrated Block still copies the TAG value to the Split CompleTIon Table, as well as the comparison completion and the TAG in the table. But it does not check if each TAG is unique.
At the same time, the user logic cannot issue a new Non-Posted transaction request when the number of TAGs issued reaches the limit of the Split Completion Table, 64, regardless of the mode of operation. Unless there is a complete completion return, the TAG is released and the Split Completion Table has a location to accommodate the new TAG, and the new Non-Posted transaction request will be accepted. Even in the external TAG management mode, this TABLE capacity limit cannot be released by the setting. Figure 1 shows a simulated waveform using the external TAG management mode. It can be seen that when the Non-Posted transaction request reaches 64, s_axis_rq_tready becomes 1, and the user cannot issue a new Non-Posted transaction request. Since the limit of 64 is less than the maximum value of 256 that can be reached by the specification, the user must pay attention. Especially in high LATENCY systems, in order to improve performance, you must issue as many transaction requests as possible. In this case, the system must be carefully designed to reduce the LATENCY so that the TAG value is not exhausted.
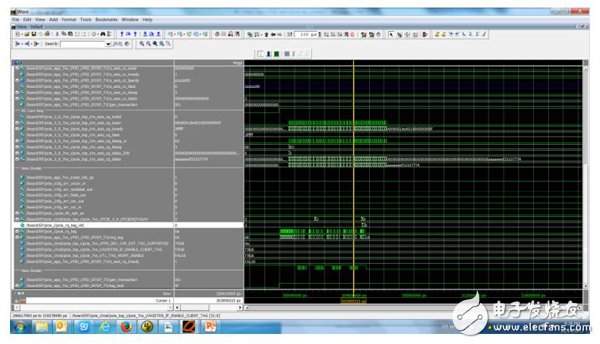
In the external TAG management mode, since the Gen3 Integrated Block does not check the uniqueness of each Non-Posted transaction request, even if each Non-Posted transaction request uses the same TAG value, they can be issued. This can also be seen in Figure 1 simulation waveform. However, it will not be possible to identify which Non-Posted transaction corresponds to the completion, so when using the external TAG management mode, the user logic must be very careful about the management of the TAG.
Bitmain is the world's leading digital currency mining machine manufacturer. Its brand ANTMINER has maintained a long-term technological and market dominance in the industry, with customers covering more than 100 countries and regions. The company has subsidiaries in China, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Kazakhstan and other places.
Bitmain has a unique computing power efficiency ratio technology to provide the global blockchain network with outstanding computing power infrastructure and solutions. Since its establishment in 2013, ANTMINER BTC mining machine single computing power has increased by three orders of magnitude, while computing power efficiency ratio has decreased by two orders of magnitude. Bitmain's vision is to make the digital world a better place for mankind.
Bitmain Antminer:Bitmain Antminer KA3 (166Th),Bitmain Antminer L7 (9.5Gh),Bitmain Antminer Z15,Bitmain Antminer D7 (1286Gh),
Bitmain Antminer S19 XP (140Th),Bitmain Antminer E9 (2.4Gh),Bitmain Antminer Z11,Bitmain Antminer S3,Bitmain Antminer L3+ (504Mh)
Bitmain Antminer,S19 Pro Hyd 198T,antminer bitmain,antin s19j,antminer miner
Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hkcryptominer.com