Editor's note
In general, the copper precipitation reaction of a lithium ion battery occurs in the negative electrode. The possibility of overdischarge, the reverse charging of the battery during the manufacturing process, and the large current discharge of the battery when a local short circuit occurs locally may cause the copper precipitation reaction to occur.
With the wide application of lithium-ion power batteries, the pure electric vehicles loaded in the first batch of power batteries have also ran for seven or eight years. During this period, various failures will occur. One of the copper analysis begins, the conclusions are obtained through experimental verification, and some suggestions are given to prevent such failures.

In general, the copper precipitation reaction of a lithium ion battery occurs in the negative electrode. The possibility of overdischarge, the reverse charging of the battery during the manufacturing process, and the large current discharge of the battery when a local short circuit occurs locally may cause the copper precipitation reaction to occur.
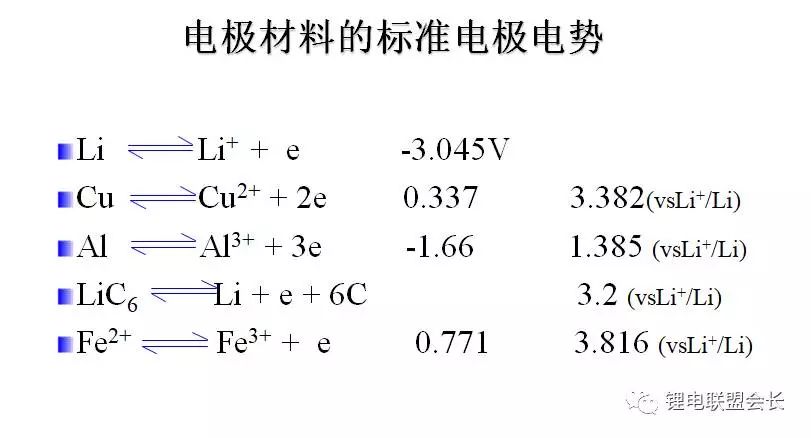
Generally, there are four processes for the copper evolution reaction. First, the dissolution of the copper foil is oxidized, then the copper is precipitated on the surface of the negative electrode, and then the copper is dissolved, passes through the separator, and precipitates on the positive electrode.
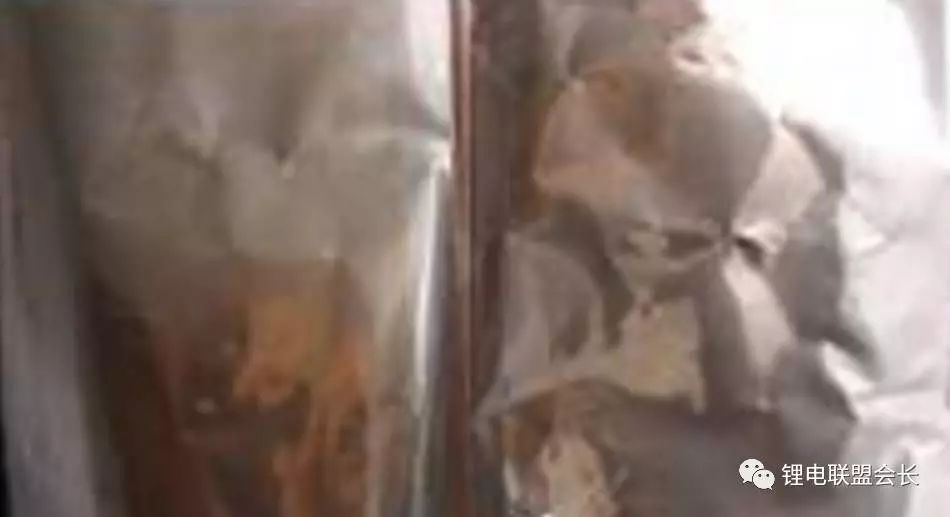


As can be seen from the above figure, copper has been precipitated on the positive electrode, and the copper foil of the negative electrode has also been oxidized, indicating that copper precipitation is very serious. The voltage of this battery has been less than 1V and completely failed.
For the occurrence of failure, it is initially found that the large current overdischarge of individual cells may be caused by the SOC inconsistency. The following design experiments are verified. The experimental steps are as follows:
1. Take three lithium-ion power batteries, the SOC is set to 40%, 60%, 80%, and three batteries are connected in series for large current discharge;
2. Each time the battery is placed for a period of time, the voltage internal resistance of the battery is measured;
3. Continue with the previous two steps;
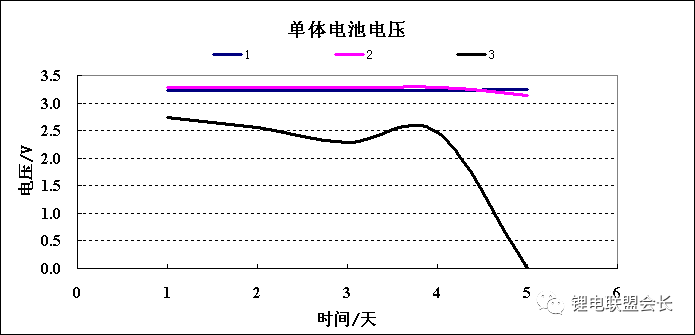
After several high current cycles, the low SOC power battery showed a significant voltage drop, and an abnormal battery was dissected.
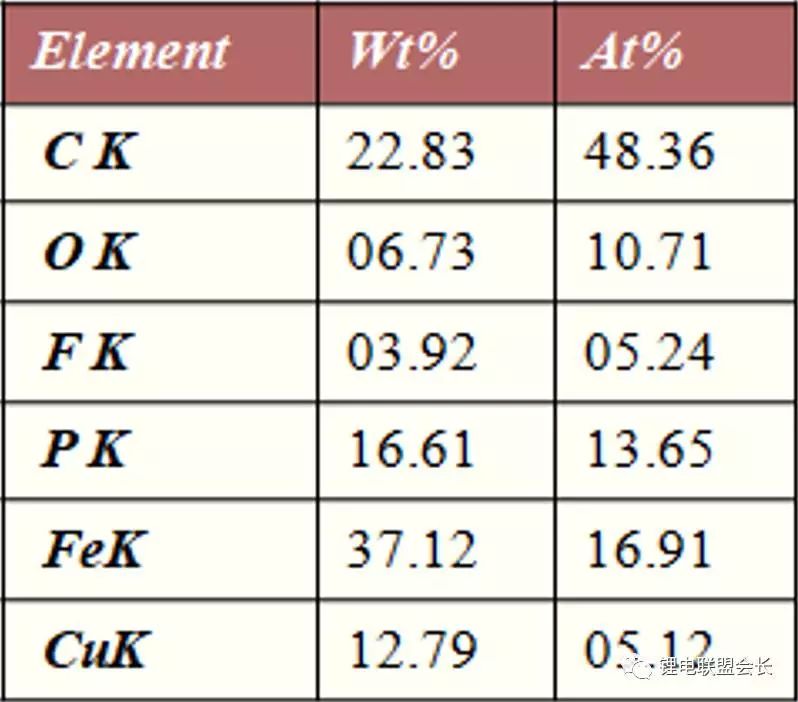


Anatomically, a partial short-circuit point was found. The EDS analysis of the separator at the short-circuit point revealed the presence of copper, indicating that the copper-out reaction had occurred, indicating that copper was formed during the actual use due to inconsistent SOC conditions during high-current discharge. The reaction is complicated when used in an actual process, so it is necessary to improve the consistency of the lithium ion power battery and prevent such a failure mode from occurring.
10W Wireless Charger,Car Wireless Charger,10W Wireless Charger,15W Wireless Phone Charger
Comcn Electronics Limited , https://www.comencnspeaker.com