Special Mode # 1: 3 State OutputsWhen the SYSCLK pin is held high for 193 RCLK periods, all output pins, including the parallel port are 3-stated.
Special Mode # 2: Allow Access Between Framer and LIU on Transmit SideWriTIng 40hex to the TEST resister will invoke this mode. When enabled, the internal TLINK node is TIed to the TSER pin. This access is useful in applications where it is desired to purposely corrupt the data stream before it is to be transmitted out onto the T1 line via TTIP and TRING pins. There is an exact delay from the TSER pin to the bipolar outputs of the formatter so the user has the ability to know when the needed bits appear at RCLK and RLINK pins. This delay is 10 TCLK periods.
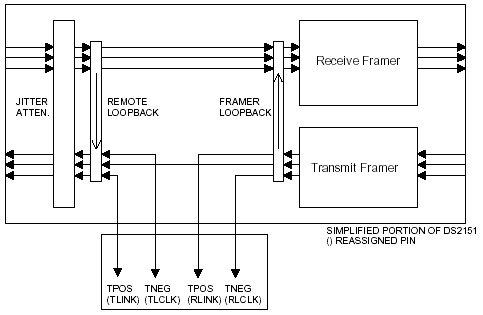
Mode 2: DS2151 Special mode to allow access to transmit bipolar data stream.
Special Mode # 3: Tap the Transmit "Receive Bipolar Data StreamWriting 60hex (REV B ONLY) to the TEST register will invoke this mode. When enabled, the internal TLINK node is tied to the TSER pin.
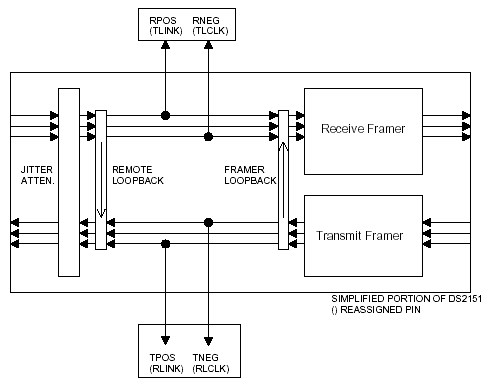
Mode 3: DS2151 Special mode to tap the transmit receive bipolar data streams.
Special Mode # 4: Asynchronous, Elastic Stores OperationWriting 07hex (REV B ONLY) to the TEST Register will invoke this mode.
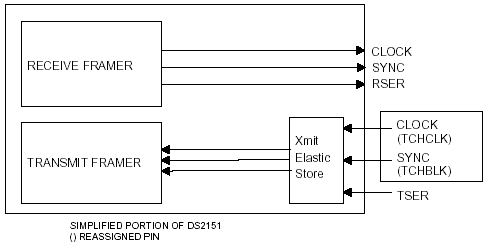
Mode 4: DS2151 Special mode to allow asynchronous backplane clocks.
NOTE: When using Special Mode # 4 and polling data on a multi-frame boundary, an external elastic store (DS2175) should be used instead of the transmit side elastic store of the DS2151. The internal elastic store built into the DS2153 can not release data on a multi-frame boundary. A DS2175 has the ability to sync on multi-frame pulses and therefore should be used instead.
Special Mode # 5: LIU Bypass
Writing 60hex (REV A), 20hex (REV B) to the TEST register will invoke this mode. When enabled, the internal TLINK node is tied to the TSER pin.
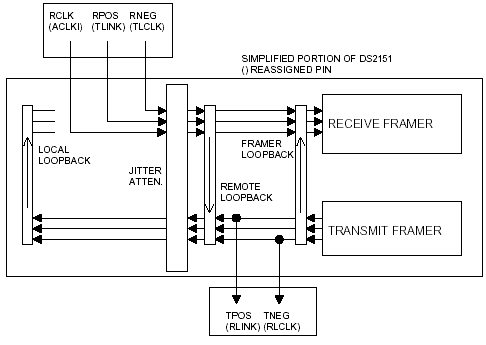
Mode 5: DS2151 Special mode to bypass the LIU.
Speakers are one of the most common output devices used with computer systems. Some speakers are designed to work specifically with computers, while others can be hooked up to any type of sound system. Regardless of their design, the purpose of speakers is to produce audio output that can be heard by the listener.
Speakers are transducers that convert electromagnetic waves into sound waves. The speakers receive audio input from a device such as a computer or an audio receiver. This input may be either in analog or digital form. Analog speakers simply amplify the analog electromagnetic waves into sound waves. Since sound waves are produced in analog form, digital speakers must first convert the digital input to an analog signal, then generate the sound waves.
The sound produced by speakers is defined by frequency and amplitude. The frequency determines how high or low the pitch of the sound is. For example, a soprano singer's voice produces high frequency sound waves, while a bass guitar or kick drum generates sounds in the low frequency range. A speaker system's ability to accurately reproduce sound frequencies is a good indicator of how clear the audio will be. Many speakers include multiple speaker cones for different frequency ranges, which helps produce more accurate sounds for each range. Two-way speakers typically have a tweeter and a mid-range speaker, while three-way speakers have a tweeter, mid-range speaker, and subwoofer.
Speaker System,Magnet Speaker Acoustic,Moving Coil Loudspeaker,Metal Frame Mylar Speaker
Jiangsu Huawha Electronices Co.,Ltd , https://www.hnbuzzer.com