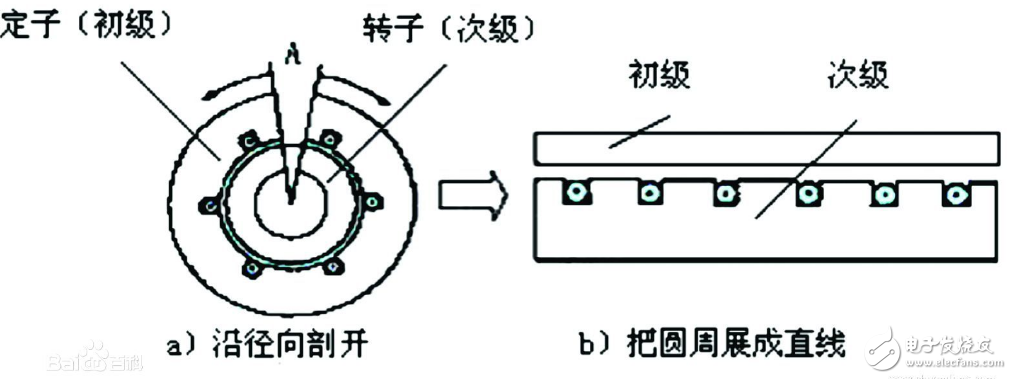
A linear motor is a transmission that converts electrical energy directly into linear motion mechanical energy without the need for any intermediate conversion mechanism. It can be seen as a rotating motor that is cut radially and flattened.
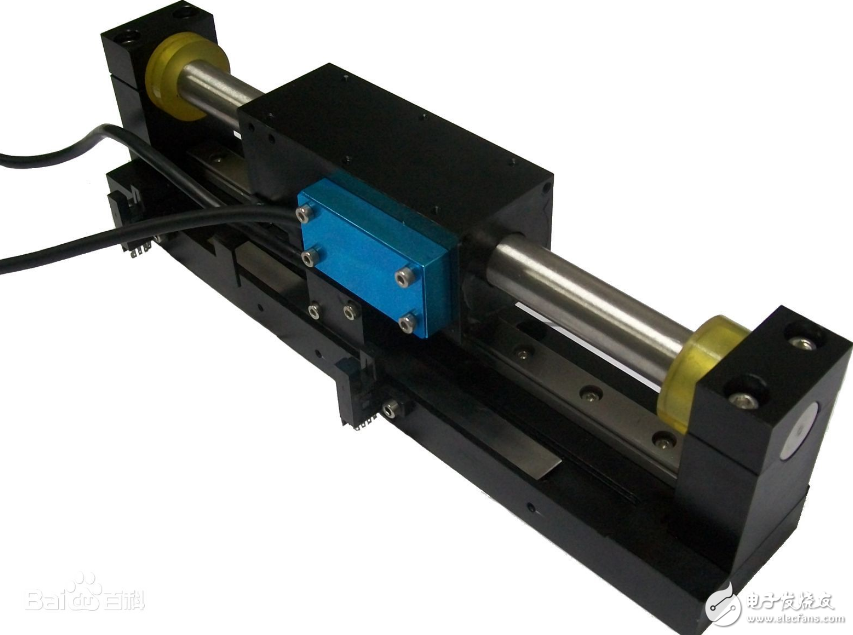
Linear motors are also called linear motors, linear motors, linear motors, and push rod motors. The most common types of linear motors are flat and U-groove, and tubular. The typical composition of the coil is three-phase, and the Hall element realizes brushless commutation.
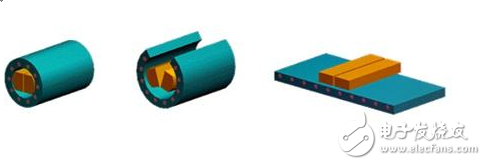
The linear motor of this figure clearly shows the internal winding of the mover (rotor). Magnets and tracks. The mover presses the coil with an epoxy material. Moreover, the magnetic track is to fix the magnet on the steel.
Linear motors are often simply described as rotating motors that are flattened and work the same way. A forcer (rotor) is made by compressing a coil of epoxy together; the track is a magnet (usually a high-energy rare earth magnet) that is attached to the steel. The mover of the motor includes a coil winding, a Hall element circuit board, a thermistor (temperature sensor monitor temperature), and an electronic interface. In a rotating electrical machine, the mover and the stator require a rotating bearing to support the mover to ensure an air gap of the relatively moving portion. Similarly, linear motors require linear guides to maintain the position of the mover in the magnetic field generated by the track. The encoder of the rotary servo motor is mounted on the on-axis feedback position. The linear motor needs to feed back the linear position feedback device--linear encoder, which can directly measure the position of the load and improve the position accuracy of the load.
The control of the linear motor is the same as that of the rotary motor. Like a brushless rotary motor, there is no mechanical connection between the mover and the stator (brushless). Unlike the rotary motor, the rotor rotation and the stator position remain fixed. The linear motor system can be a magnetic or thrust coil (most of the positioning). The system application is that the track is fixed and the thrust coil is moved). For a motor that uses a thrust coil, the weight and load ratio of the thrust coil are small. However, high flexibility cables and their management systems are required. A motor that uses a magnetic track not only has to withstand the load but also withstands the quality of the track, but does not require a cable management system.
Similar electromechanical principles are used on linear and rotary motors. The same electromagnetic force produces a torque on the rotating electrical machine that produces a linear thrust action on the linear motor. Therefore, linear motors use the same control and programmable configuration as rotary motors. Linear motors can be in the form of flat and U-grooves, and tubular. Which configuration is best suited to the specifications and working environment of the actual application.
Linear motor working principleThe side that evolved from the stator is called the primary, and the side that evolved from the rotor is called the secondary. In practical applications, the primary and secondary are manufactured to different lengths to ensure that the coupling between the primary and secondary remains constant over the desired range of travel. The linear motor can be a short primary long secondary or a long primary short secondary. Considering the manufacturing cost and operating cost, take the linear induction motor as an example: when the primary winding is connected to the AC power source, a traveling wave magnetic field is generated in the air gap, and the secondary will induce an electromotive force and generate a current under the cutting wave magnetic field cutting. The current reacts with the magnetic field in the air gap to generate electromagnetic thrust. If the primary is fixed, the secondary moves linearly under the action of the thrust; otherwise, the primary performs a linear motion. Drive Control Technology for Linear Motors A linear motor application system must have not only a linear motor with good performance, but also a control system that can achieve technical and economical requirements under safe and reliable conditions. With the development of automatic control technology and microcomputer technology, there are more and more control methods for linear motors.

The research on linear motor control technology can be basically divided into three aspects: one is traditional control technology, the other is modern control technology, and the third is intelligent control technology.
Traditional control technologies such as PID feedback control and decoupling control have been widely used in AC servo systems. Among them, PID control implies information in the dynamic control process and has strong robustness. It is the most basic control method in AC servo motor drive system. In order to improve the control effect, decoupling control and vector control techniques are often used. The traditional control technique is simple and effective under the condition that the object model is determined, does not change, and is linear, and the operating conditions and operating environment are determined to be constant. However, in high-performance micro-feeding high-performance applications, changes in object structure and parameters must be considered. A variety of non-linear effects, changes in the operating environment and environmental disturbances, such as time-varying and uncertain factors, can achieve satisfactory control results. Therefore, modern control technology has attracted a lot of attention in the research of linear servo motor control. Commonly used control methods are: adaptive control, sliding mode variable structure control, robust control and intelligent control. It mainly combines fuzzy logic, neural network with existing mature control methods such as PID and H∞ control to learn from each other to obtain better control performance.
Linear motor advantages(1) The structure is simple. The tubular linear motor does not need to go through the intermediate conversion mechanism to directly generate linear motion, which greatly simplifies the structure, reduces the motion inertia, greatly improves the dynamic response performance and positioning accuracy, and also improves the reliability, saves the cost, and makes the manufacturing and maintenance more Simple. Its primary and secondary can be directly part of the organization, and this unique combination makes this advantage even more apparent.
(2) Suitable for high speed linear motion. Because there is no constraint on centrifugal force, ordinary materials can achieve higher speeds. Moreover, if the air gap or the magnetic pad is used to store the gap between the primary and secondary, there is no mechanical contact during the movement, and thus the moving part has no friction and noise. In this way, the transmission components are not worn, which can greatly reduce the mechanical loss and avoid the noise caused by the streamers, cables, gears and pulleys, thereby improving the overall efficiency.
(3) The primary winding utilization is high. In tubular linear induction motors, the primary winding is pie-shaped and has no end windings, so the winding utilization is high.
(4) No lateral edge effect. The transverse effect refers to the weakening of the magnetic field at the boundary due to the lateral breaking, and the cylindrical linear motor has no lateral break, so the magnetic field is evenly distributed along the circumference.
(5) It is easy to overcome the problem of single-sided magnetic pull. The radial pulling forces cancel each other out, and there is basically no problem of single-sided magnetic pulling force.
(6) Easy to adjust and control. By adjusting the voltage or frequency, or replacing the secondary material, different speeds and electromagnetic thrusts can be obtained, which is suitable for low-speed reciprocating applications.
(7) Strong adaptability. The primary core of the linear motor can be sealed with epoxy resin, which has good anti-corrosion and moisture-proof properties, and is easy to use in the environment of moisture, dust and harmful gases. It can also be designed into various structures to meet the needs of different situations. .
(8) High acceleration. This is a linear motor drive that offers a significant advantage over other lead screws, timing belts and rack and pinion drives.
Power 12W ,output voltage 3-12V, output current Max 1A, 6 dc tips. We can meet your specific requirement of the products, like label design. The material of this product is PC+ABS. All condition of our product is 100% brand new.
Our products built with input/output overvoltage protection, input/output overcurrent protection, over temperature protection, over power protection and short circuit protection. You can send more details of this product, so that we can offer best service to you!
12W Wall Adapter, 12W Wall Power Supply,12W Power Cord In Wall, 12W Wall Power Adapter
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szwaweischarger.com